Macros Explained in 2026: The Ultimate Nutrition Guide
The Complete Nutrition Guide in 2026: Macros Explained
Macros is a term that is likely to seem confusing or even technical or even intimidating to you especially in case you are new to the world of fitness or nutrition. The fact is that knowing macros is one of the easiest and most effective solutions that you can employ to change your body, health and performance in 2026. You do not need to starve, be on extreme diets and feel guilty about food. You just need clarity.
This is an easy-to-understand guide that decomposes macros. You will have the perfect idea, by the end, what macros are, how they function, how to compute them and where to apply them in life real-life, without obsessing or burning out.
What Are Macros?
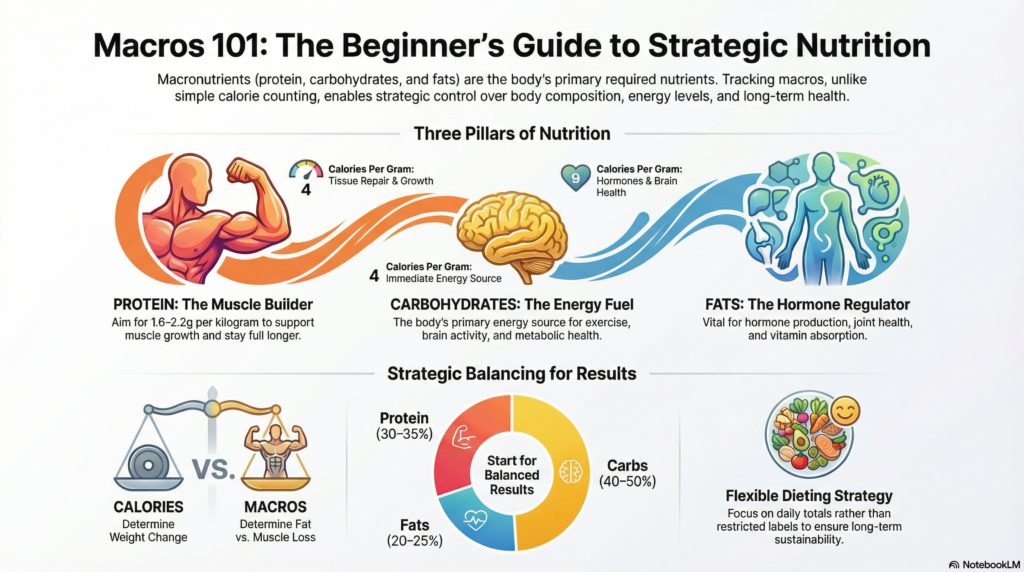
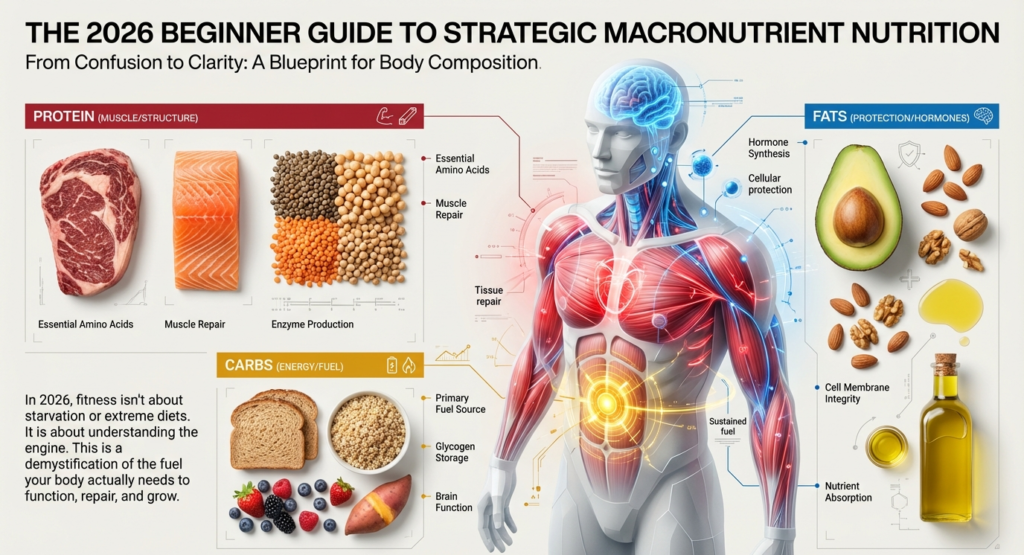
Macros are also known as macronutrients; the three broad nutrients that your body requires in huge proportions to act, develop and operate. They are protein, carbohydrates and fats. All the food you consume consists of either one or a combination of these macros.
Macronutrients contain calories unlike micronutrients such as vitamins and minerals. Calories are nothing but energy and your body burns the energy for movement, recovery, hormone production, brain activity, and survival. Macros is not about the amount of calories you consume but rather what you consume.

Why Macros are More Important than Diet Labels
In 2026, it will no longer be about which one is better keto, low-carb, vegan, or paleo. Those are just frameworks. The only thing that counts is the amount of protein, carbs and fats that you take in a day.
Two individuals may consume equal amounts of calories and receive entirely varying outcomes in lieu of their macro balance. One can lose weight and become a muscle, and the other one can grow fatter. It is macros that dictate the body composition, and not labels on food or diets.
When you comprehend macros, then you are free. You will no longer be afraid of foods but make wise decisions.
Protein: The Macro of Muscle Building.
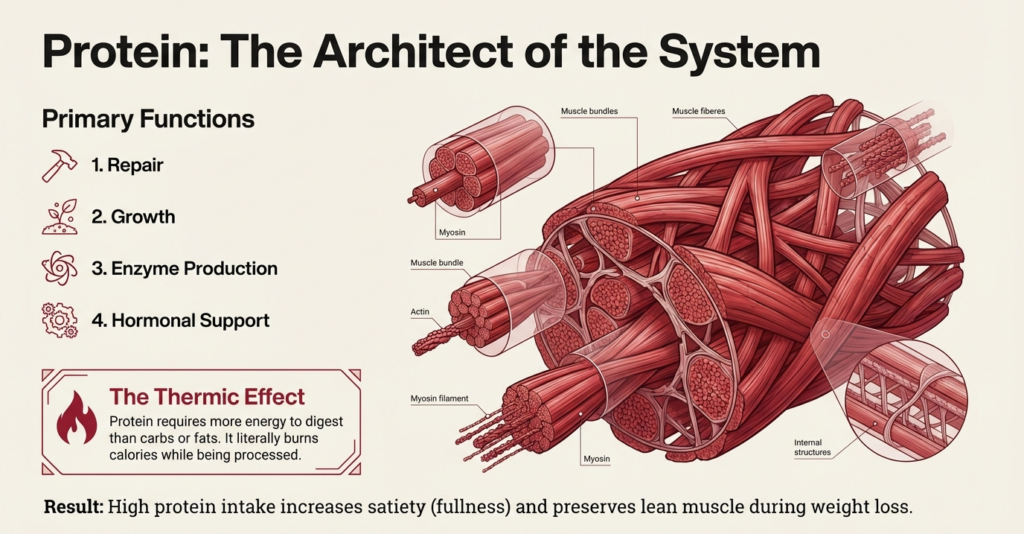
Protein is what helps repair, grow, improve immunity, produce enzymes and support hormones. It is the biggest macro to begin with since it has a direct influence on muscle tone and fat loss.
Consuming adequate amounts of protein makes you fuller, heals quicker and helps you retain lean muscle mass when you lose weight. Protein is also known to possess higher thermic effect, that is, it uses more calories to be digested in your body as compared to carbs or fats.
By the way, typical sources of proteins are eggs, chicken, fish, paneer, tofu, lentils, whey protein, Greek yogurt, and lean meat.
Protein Requirement : How Much?
As of 2026, the protein intake recommendation supported by research should be 1.6-2.2 grams of protein per kilogram of bodyweight in beginners. When you are aiming at losing fat, then be more towards the high end. When you are lazy the bottom end is at work.
As an illustration, an inexperienced person with a weight of 70 kgs is expected to stay at 110-150 grams of protein every day. This can be very expensive but when divided into meals it can be affordable.
Protein timing is flexible. The overall amount of food one eats per day is much more important than specific times of the day.

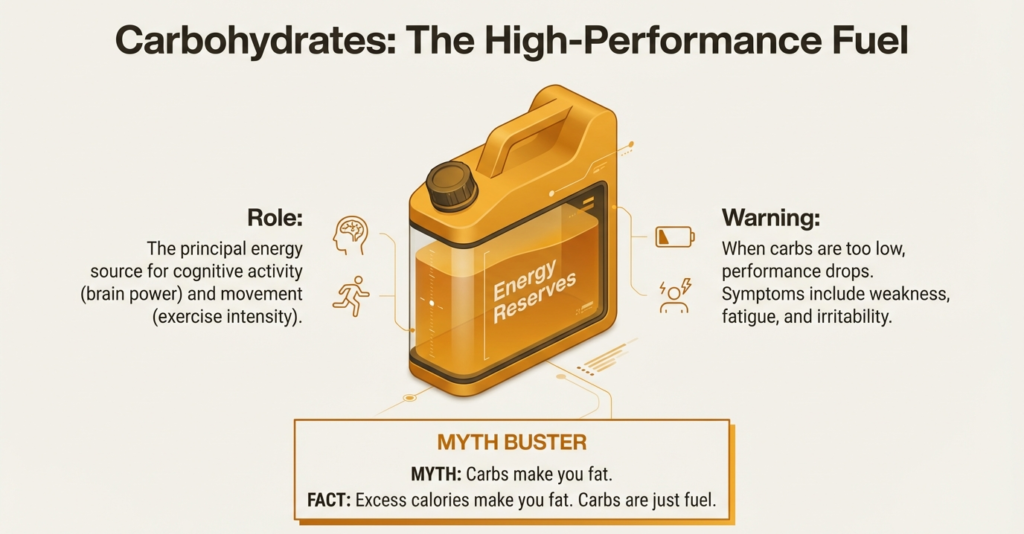
Carbohydrates: The Fuel of your Body
The principal source of energy to the body is the carbohydrates. They power exercise, cognitive activity and energy. Although it has taken several years to discover that misinformation, carbs are not the fattening food per se.
The only problem with the carbs is that they do not contribute to fat gain unless they are ingested in excess calorie amounts. They enhance performance, recoveries, mood, metabolic health when properly used. When the carbs are too low beginners tend to feel weak, fatigued or irritable.
Some of the healthy sources of carbohydrates are rice, roti, oats, potatoes, fruits, and vegetables, millets, and legumes.
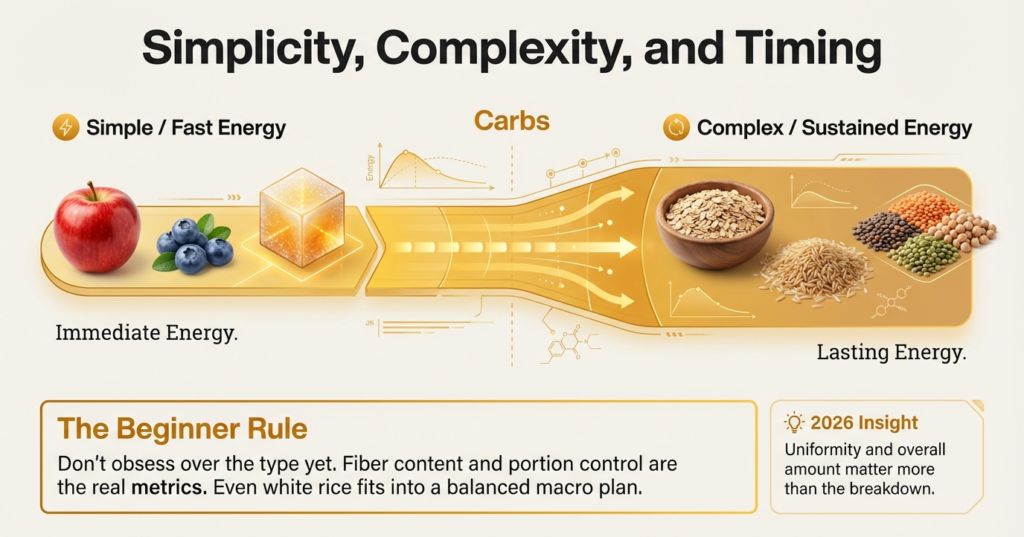
Knowing Simple vs Complex Carbs.
Carbohydrates have been typically classified as simple and complex. The simple carbs are easy to digest and offer immediate energy whereas the complex carbs are slow to digest and offer lasting energy.
In the real world, fiber content and portion control are more important than carb labels. Fruits are rich in nutrients and healthy although they contain simple sugars. It is possible to include white rice even in a well-balanced macro plan.
To the novice, the uniformity and the overall amount of carb eaten are more important than the breakdown of carbs.
Fats: The Necessary, Yet Misconceived
Fat diet is essential in producing hormones, maintaining joints, absorption of vitamins, and the brain. Excessively low fat intake is detrimental to testosterone levels, recovery and long term health.
Fats contain high energy which is 9 calories per gram as compared to 4 calories per gram protein and carbs. This is why it is significant to control portions, but not to consider fats unhealthy.
The healthy sources of fats are nuts, seeds, olive oil, ghee, avocados, egg yolks, and fatty fish.

How Much Fat Should You Eat?
An initial recommendation would be 20 30 percent of total daily fat calories. It should not be long before going below this without supervision.
Using an illustration of a 2,000-calorie diet, fat intake would be between 4565 grams per day. Your remaining calories can be allocated to either protein or carbohydrates depending on your intended purpose.
Balance is key. Fat is necessary, however, when consumed in excess, it may readily lead to surplus calories.

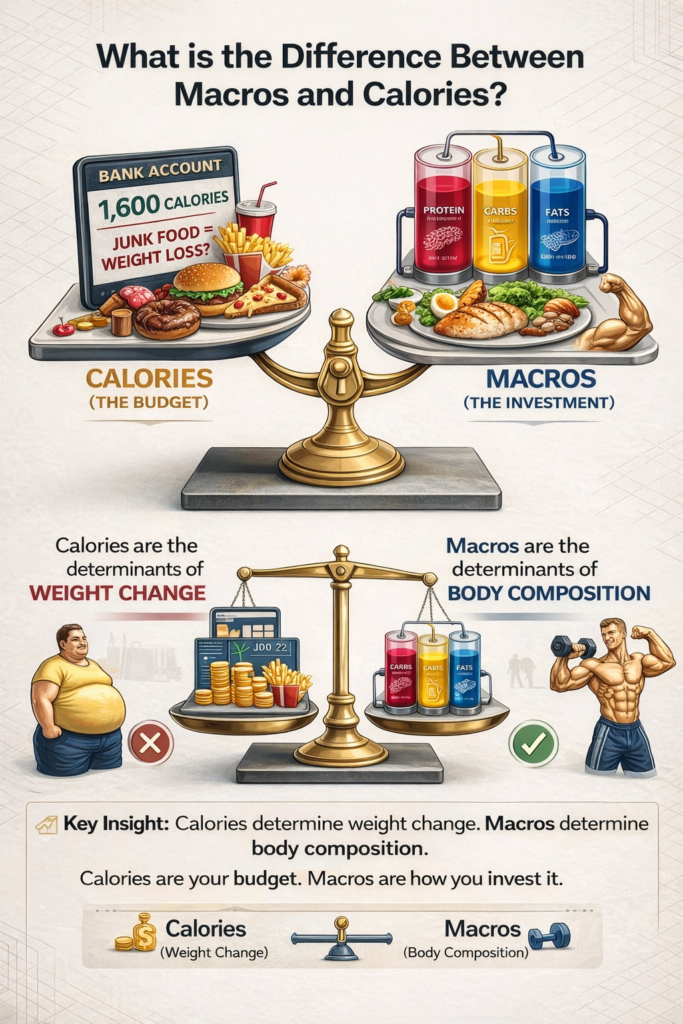
What is the Difference between Macros and Calories?
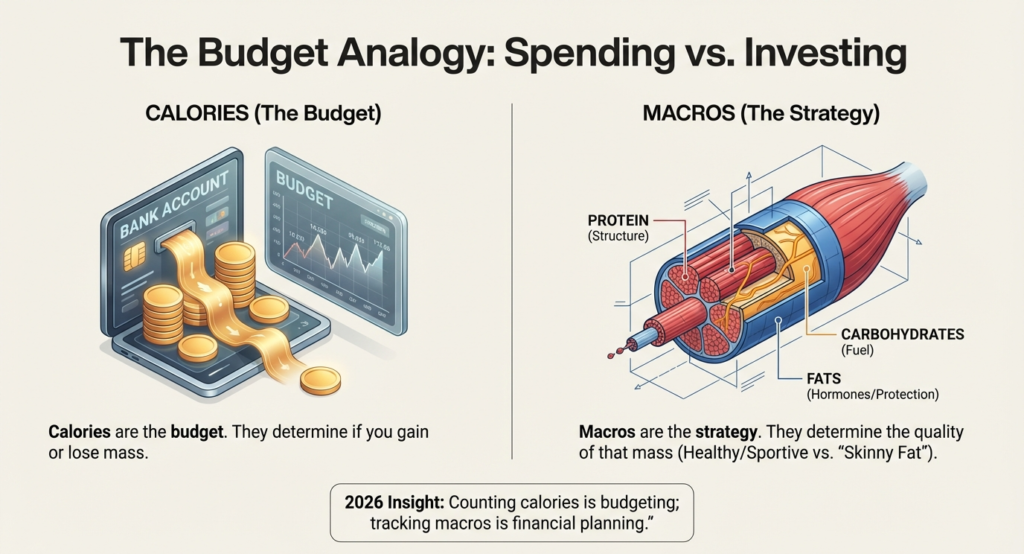
Calories are the determinants of weight change whereas macros are the determinants of body composition. Eating junk food, you can lose weight, when the calorie consumption is low, but you cannot look healthy or sportive.
Macros make sure that weight loss is achieved through fat and not muscle. They also make you build muscle, without losing too much fat. That is why counting calories is weak as compared to tracking macros.
Consider calories as the budget and the macros as the way you spend.
Method How to Calculate Your Macros
Begin by determining the amount of calories you need on any given day based on the weight of your body, the activity level and the goal. After you have set the calories, break them down into macros.
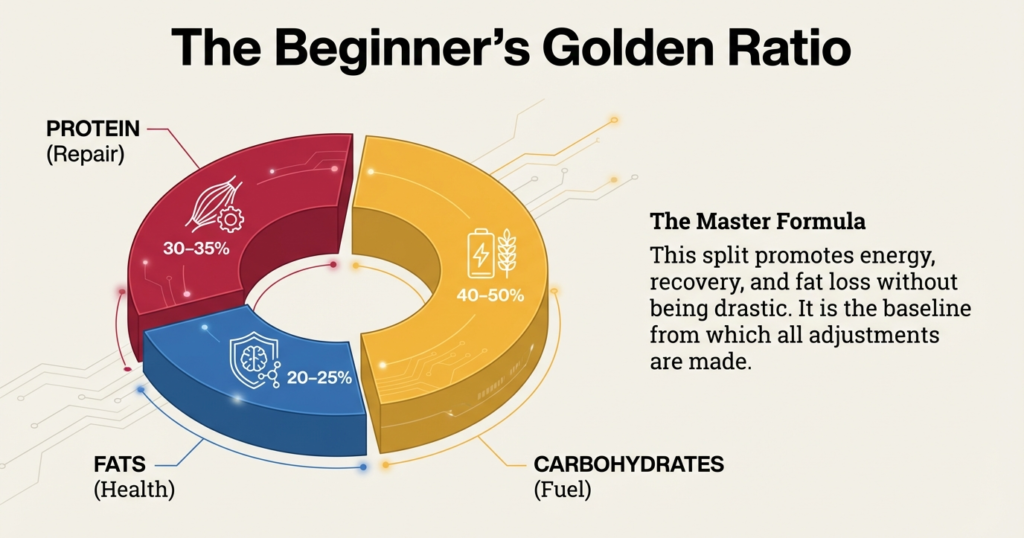
The basic amateur split resembles one shown below:
Protein: 30–35% of calories
Carbohydrates: 40–50% of calories
Fats: 20–25% of calories
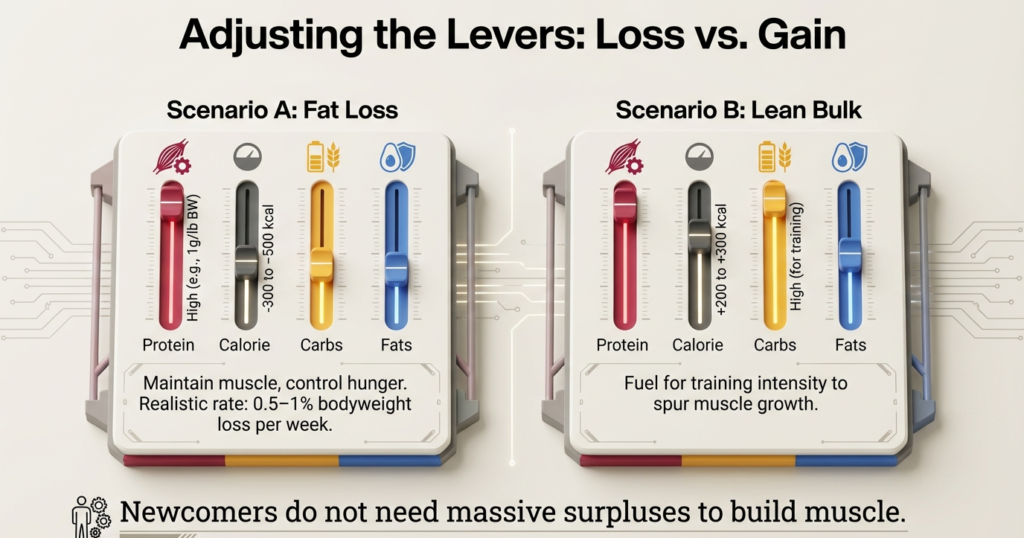
The ratio is most suitable with those who are new and promotes energy, recovery and fat loss without being too drastic.Macros to lose fat (Easy to follow)
To lose fat set up a small deficit in calories combining with high protein content. This maintains muscle and makes the hunger in check.
Do not rudely reduce the carbs or fats. Severe restriction causes fatigue, cravings and relapse weight gain. Gradual, long-term weight loss is always the winner.
The realistic rate of fat loss is between 0.5 and 1 percent bodyweight per week. Something quicker tends to compromise muscle.
Protein Macros (Lean Bulking)
To build muscle, consume a small energy deficit of sufficient protein and carbohydrates. Carbs provide energy to the intensity of training, which spurs muscle development.
Newcomers do not require huge excesses. Even 200-300 additional calories daily suffices to gain muscle without too much fat accumulation.
Protein is kept at constant levels, carbs are raised slightly, and fats are kept in moderation.
Flexible Dieting: Eat Whatever You Like
Macros allow flexibility. You may consume rice, roti, chocolate or pizza, as you please-so long as your macros are not compromised.
Good and bad foods do not exist, just foods that suit your macros better or worse. The time interval is more important than one meal.
This will enhance compliance, psychological well-being, and ultimate relapse.

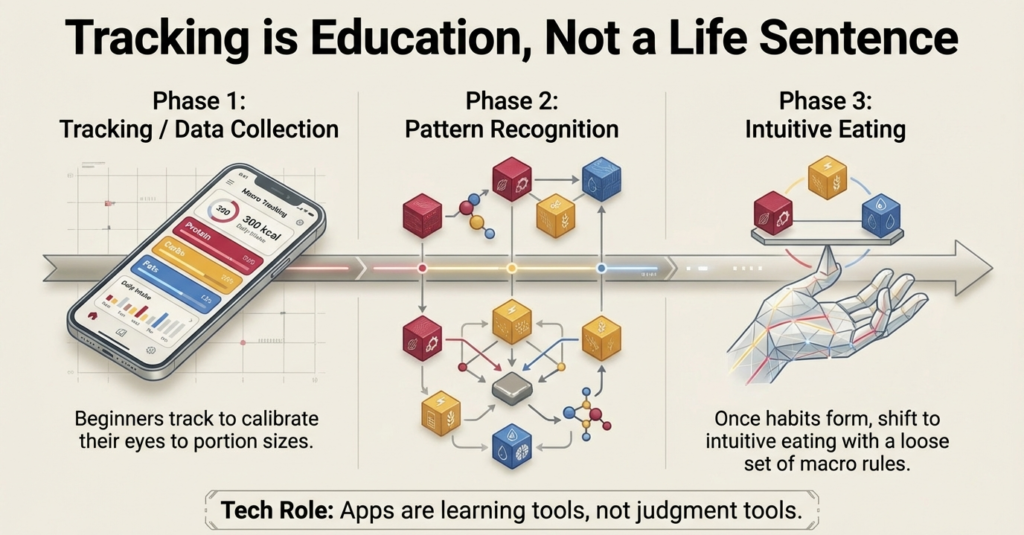
Should you monitor your Macros in a Daily Basis?
Macros tracking is an aid and not a life term. Novices have the advantage of monitoring over a few months to develop the consciousness of portions and food options.
After forming habits, a significant number of people switch to the intuitive eating style with a loose set of macro rules. Education, not obsession is a goal.
Tracking apps should be used as learning tools and not as judgment tools.
Macros in 2026: What’s New?
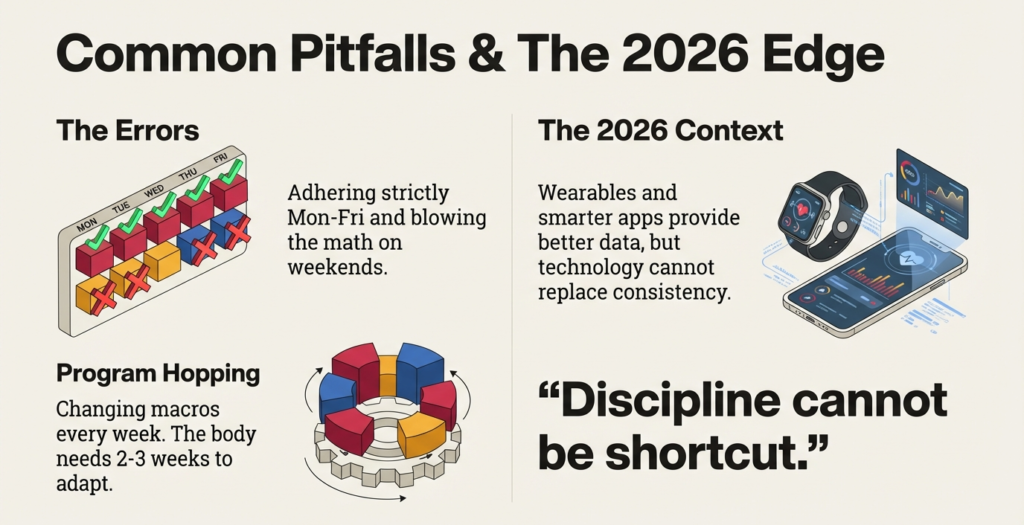
Personalized nutrition is more developed in 2026, although the basics are the same. Apps are smarter, food databases more decent, and wearable integration helps to estimate the energy requirements more accurately. Protein, carbs, fats and calories are all the same regardless of new technology. Discipline and consistency cannot be short cut.The fundamentals will never become obsolete.
Macro Beggared Follies:
Most novices eat too little protein, consume excess fats and are afraid of carbs. There are those who follow the right pattern, weekday, weekday, weekend, binge.
The other error is to switch macros on a weekly basis. Allow at least 2-3 weeks to give your plan before changing. Your body has to take time.
Perfection is nothing but simplicity. Since hard work is better than being radical.
Last Impression: Use Simple Terms
Macros are not magic. They are a smart method of consuming food. Being a beginner, do not think that you should master everything but learn. Kick it with your protein, portion and mostly whole food and be regular. Results will follow. The most ideal nutrition plan is the one you can adhere to in the long-run; and macros give you that liberty.
Read more: https://www.emro.who.int/index.php?option=com_content&view=category&layout=blog&id=1462&Itemid=2215


Gearless Physique
Physique Without Gear
Your transformation starts now. Who's with me?


